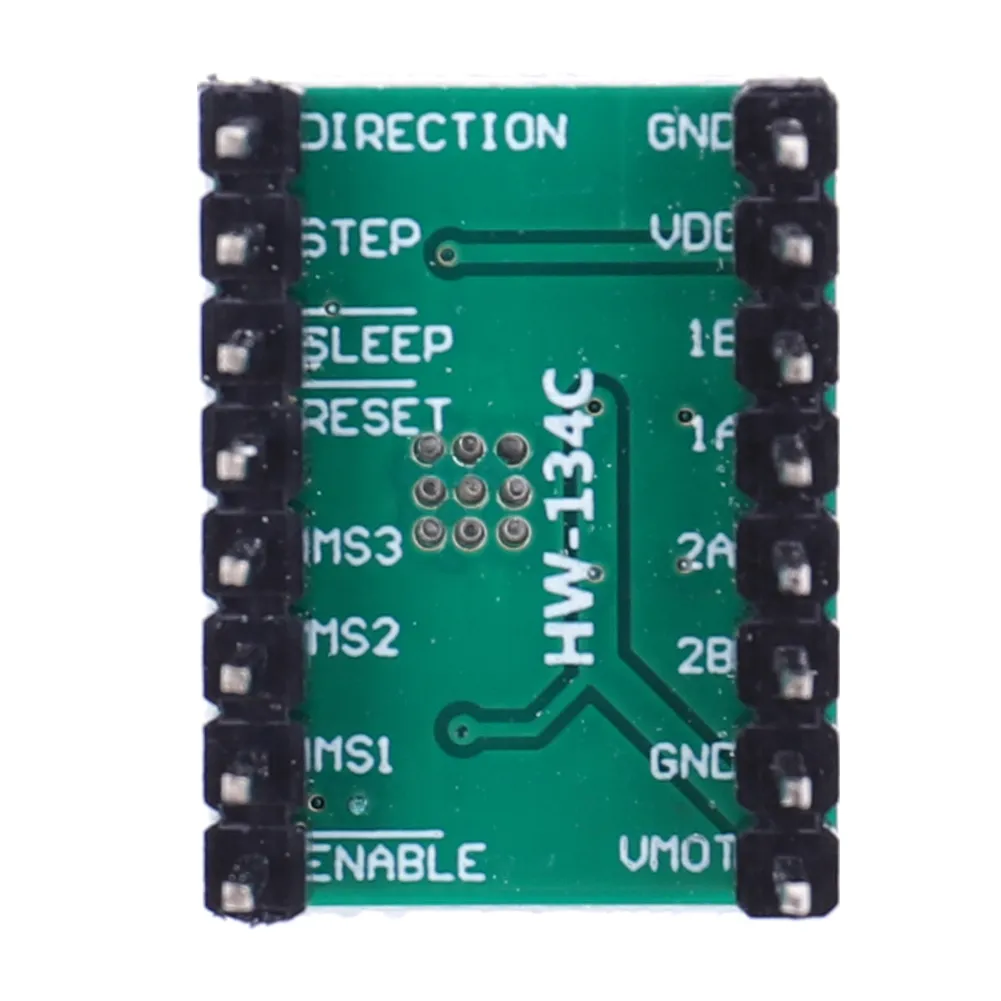
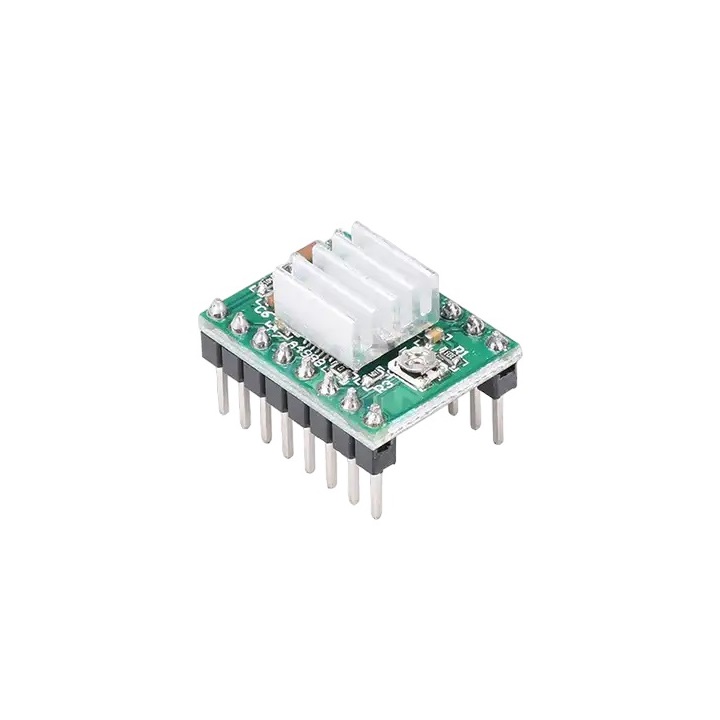
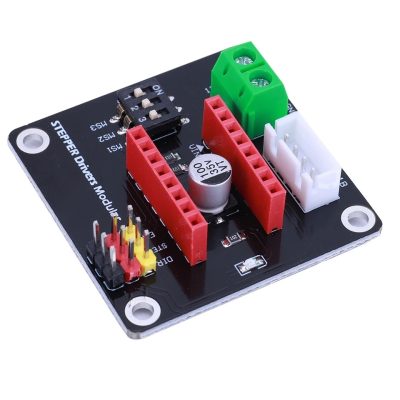
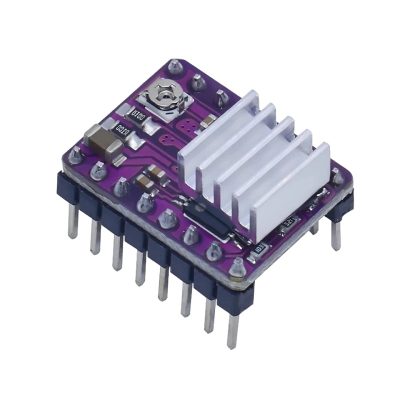
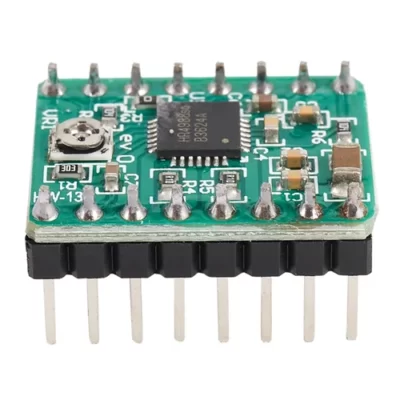
درایور استپر موتور A4988 برد سبز
۷۷,۰۰۰ تومان
موجود در انبار
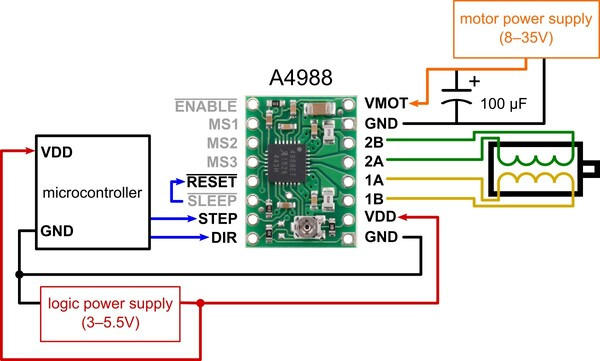
The A4988 driver Stepper Motor Driver is a complete micro-stepping motor driver with built-in converter, easy to operate.
It operates from 8 V to 35 V and can deliver up to approximately 1 A per phase without a heat sink or forced air flow (it is rated for 2 A per coil with sufficient additional cooling).
A4988 driver Stepper Motor Driver includes a fixed off-time current regulator, the regulator can be in slow or mixed decay mode.
The converter is the key to the easy implementation of the A4988.
There are no phase sequence tables, the high-frequency control interface programming etc.
The application of A4988 interface is very suitable for a complex microprocessor is not available or overload.
In the stepping operation, the chopping control in the A4988 automatically selects the current decay mode (slow or mixed).
The mix decay current control scheme can reduce the audible motor noise, increased step accuracy, and reduced power consumption.
Provide internal synchronous rectification control circuitry, in order to improve the pulse width modulation (PWM) power consumption during operation.
Features
1. Model: HW-134
2. Automatic current decay mode detection/choice.
3. Supply Voltage : 8-35 VDC.
4. Current : 1.0A (no heatsink ).
5. Current : 2.0A (with heat-sinking).
6. logic input : 3 – 5.5V .
7. Mixed with slow current decay mode.
8. The low power dissipation of synchronous rectifier.
9. Internal UVLO(ultra voltage lockout).
10. Crossover current protection.
11. Thermal shutdown circuit.
12. Ground fault protection.
13. Loading and short circuit protection.
14. The optional five-step mode: full, 1/2, 1/4, 1/8 and 1/16.
example
Although understanding the ins and outs of the A4988 and the DRV8825 may have been difficult, the advantages of using them are clear.
The code necessary for its control is extremely simple, which makes them very practical and useful components to use.
We simply have to indicate, using two digital outputs, the instant at which we want the motor to advance one step, and the direction of rotation.
The speed of rotation is controlled by the time we allow to pass between steps.
The following example rotates the stepper motor one revolution in one direction, and two in the opposite direction at a slightly higher speed.
const int dirPin = 8;
const int stepPin = 9;
const int steps = 200;
int stepDelay;
void setup() {
// Marcar los pines como salida
pinMode(dirPin, OUTPUT);
pinMode(stepPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() {
//Activar una direccion y fijar la velocidad con stepDelay
digitalWrite(dirPin, HIGH);
stepDelay = 250;
// Giramos 200 pulsos para hacer una vuelta completa
for (int x = 0; x < steps * 1; x++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(stepDelay);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(stepDelay);
}
delay(1000);
//Cambiamos la direccion y aumentamos la velocidad
digitalWrite(dirPin, LOW);
stepDelay = 150;
// Giramos 400 pulsos para hacer dos vueltas completas
for (int x = 0; x < steps * 2; x++) {
digitalWrite(stepPin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds(stepDelay);
digitalWrite(stepPin, LOW);
delayMicroseconds(stepDelay);
}
delay(1000);
}
















دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این محصول نوشته نشده است.