- پروگرامرها
- دما و رطوبت
- سایر ماژول ها
- سنسور بخار سرد
- کی پد و جوی استیک
- ماژول GPS-GPRS
- ماژول رله و سوییچ
- ماژول شبکه
- ماژول نمایشگر
- ماژول های RF
- ماژول های RFID
- ماژول های پخش صدا
- ماژول های پردازش تصویر
- ماژول های تاریخ و ساعت
- ماژول های تغذیه – ولتاژ – جریان
- ماژول های ذخیره داده
- ماژول های شتاب سنج و ژیروسکوپ
- ماژول های مبدل
- ماژول های محافظ شارژ باتری
- ماژول های مولد پالس
- ماژول ولتمتر و آمپرمتر
سنسور مغناطیس اثر هال UGN3503
۳۵,۰۰۰ تومان
موجود در انبار
19
نفر در حال مشاهده این محصول هستند!
دسته: سنسورها, مغناطیس و قطب نما
توضیحات
Hall Effect Sensor
Hall Effect sensors are used in a variety of applications and come in a variety of forms.
All exploit the fact that the strength of the magnetic field passing perpendicular to the sensor varies the output by a calculable amount.
This means that the direction of the magnetic field must be a known value, or else other variables have to be known.
The Hall Effect sensor find themselves used as current sensors, mounted in a gap in a ferrite toroid which focuses the magnetic flux.
By the voltage changes so measured, both the size of the current and its direction can be determined.
Other applications can include pipe inspections.
A pipe is exposed to a magnetic field, and the hall effect device used to look for any changes which indicate voids, impurities, or other issues in the metal.
Hall sensors are also used to sense proximity, as all moving metals will interact with magnetic flux.
In these cases, the sensor is often biased with a permanent magnet.
Applications for this can be limit sensing, rotation or speed sensing, contactless/harsh environment switches, and even automotive ignition systems.
Hall Effect sensors are also used as magnetometers, measuring the strength and direction of a magnetic field.
This includes being the basis for some electronic compasses.
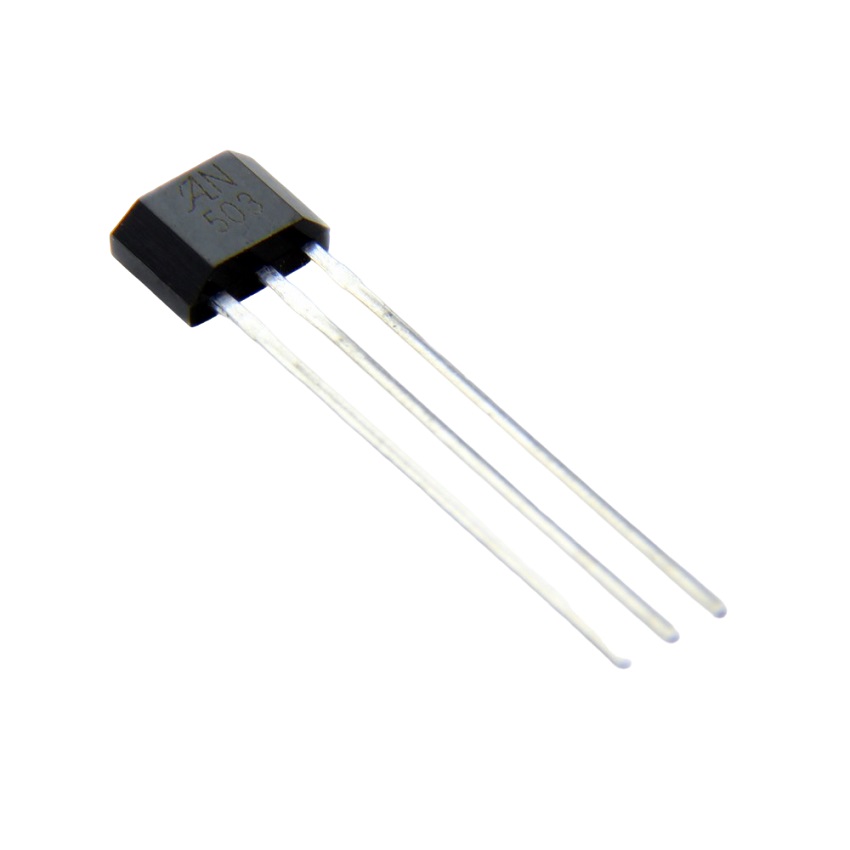
THE UGN3503
The Hall Effect sensor , is an integrated circuit consisting of a piece of semiconductor material that a current is passed through, with connections to its sides to sense the potential difference This is connected to an internal amplifier with an output stage.
In the case of the UGN3503, the output is an emitter-follower transistor.
The entire assembly is in a three-pin package with the sensor element very close to the amplifier to minimise errors.
When a magnetic field is passed through the sensor in a perpendicular plane, the output voltage changes.
Ordinarily, the output with no magnetic influence sits at around 2.5V.
With a perpendicular face south pole magnetic field, the voltage increases to a demonstrated maximum of around 3.9V.
A north pole will cause the output voltage to fall to around 1.2V demonstrated.
These workshop tests were conducted with a supply voltage of 5.0V.
In use, the UGN3503 can be powered from 4.5 to 6V, making it ideal for microcontroller applications.
It draws around 10mA constantly, the current needed to pass through the semiconductor and run the amplifier.
The three-pin package has the same lead spacing as TO92 transistors, but the package itself is a thinner Single Inline Package (SIP).
The three connections, when viewed from the printed face, are supply at the left Ground in the middle, and output on the right.
PRACTICAL APPLICATIONS
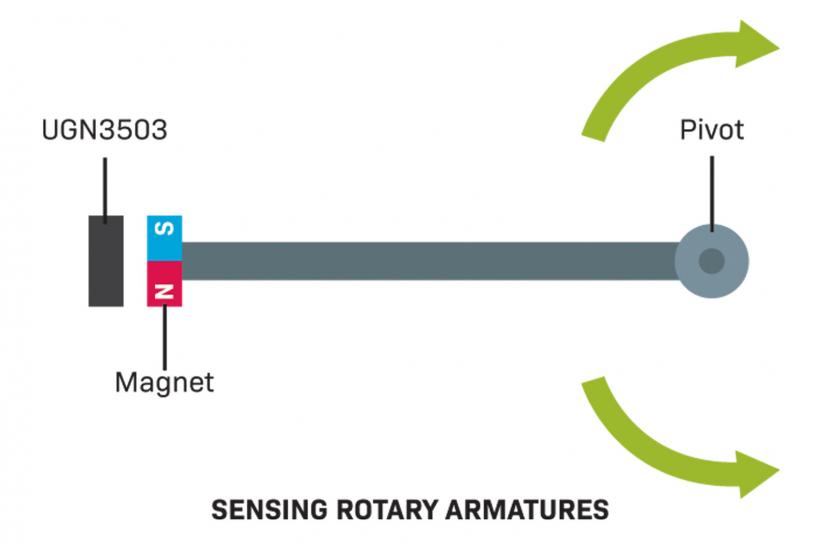
1. Sensing the position of an armature.
2. counting revolutions of a motor shaft.
3. sensing the position of a servo motor.
4. flow rate counters which involve a rotary vane in fluid (essentially a revolution counter where each revolution is a known volume of fluid).
5. proximity sensors such as a ‘door closed’ indicator.
Datasheet: UGN3503
نظرات (0)
اولین نفری باشید که دیدگاهی را ارسال می کنید برای “سنسور مغناطیس اثر هال UGN3503”
محصولات مشابه
سنسور وزن – لودسل 1 کیلوگرمی
۱۶۵,۰۰۰ تومان
ماژول سنسور گاز مونوکسید کربن MQ-9
۱۶۵,۰۰۰ تومان
فرستنده و گیرنده مادون قرمز TCRT5000
۱۵,۰۰۰ تومان
ماژول سنسور حرکت مادون قرمز HC-SR501 برد سبز
۹۶,۰۰۰ تومان
ماژول تشخیص حرکت بدن HC-SR505
ماژول تشخیص شعله KY-026
۴۷,۰۰۰ تومان
ماژول فتوسل
۴۶,۰۰۰ تومان












دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این محصول نوشته نشده است.