ماژول DC-DC افزاینده 600 وات
Description
A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage (while stepping down current) from its input (supply) to its output (load).
It is a class of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor) and at least one energy storage element: a capacitor, inductor, or the two in combination.
To reduce voltage ripple, filters made of capacitors (sometimes in combination with inductors) are normally added to such a converter’s output (load-side filter) and input (supply-side filter).
A process that changes one DC voltage to a different DC voltage is called DC to DC conversion.
A boost converter is a DC to DC converter with an output voltage greater than the source voltage.
A boost converter is sometimes called a step-up converter since it “steps up” the source voltage.
Most DC-to-DC converters are designed to move power in only one direction, from dedicated input to output.
However, all switching regulator topologies can be made bi-directionally and able to move power in either direction by replacing all diodes with independently controlled active rectification.
A bidirectional converter is useful, for example, in applications requiring regenerative braking of vehicles, where power is supplied to the wheels while driving, but supplied by the wheels when braking.
DC to DC converter is used in portable electronic devices such as cellular phones and laptop computers, which are supplied with power from batteries primarily.
Such electronic devices often contain several sub-circuits, each with its own voltage level requirement different from that supplied by the battery or an external supply (sometimes higher or lower than the supply voltage).
Additionally, the battery voltage declines as its stored energy are drained.
Switched DC to DC converters offer a method to increase the voltage from a partially lowered battery voltage thereby saving space instead of using multiple batteries to accomplish the same thing.
Most DC to DC converter circuits also regulates the output voltage.
Some exceptions include high-efficiency LED power sources, which are a kind of DC to DC converter that regulates the current through the LEDs, and simple charge pumps which double or triple the output voltage.
Specification
Input Voltage: 10 ~ 60V
Input Current: The maximum input current 10A
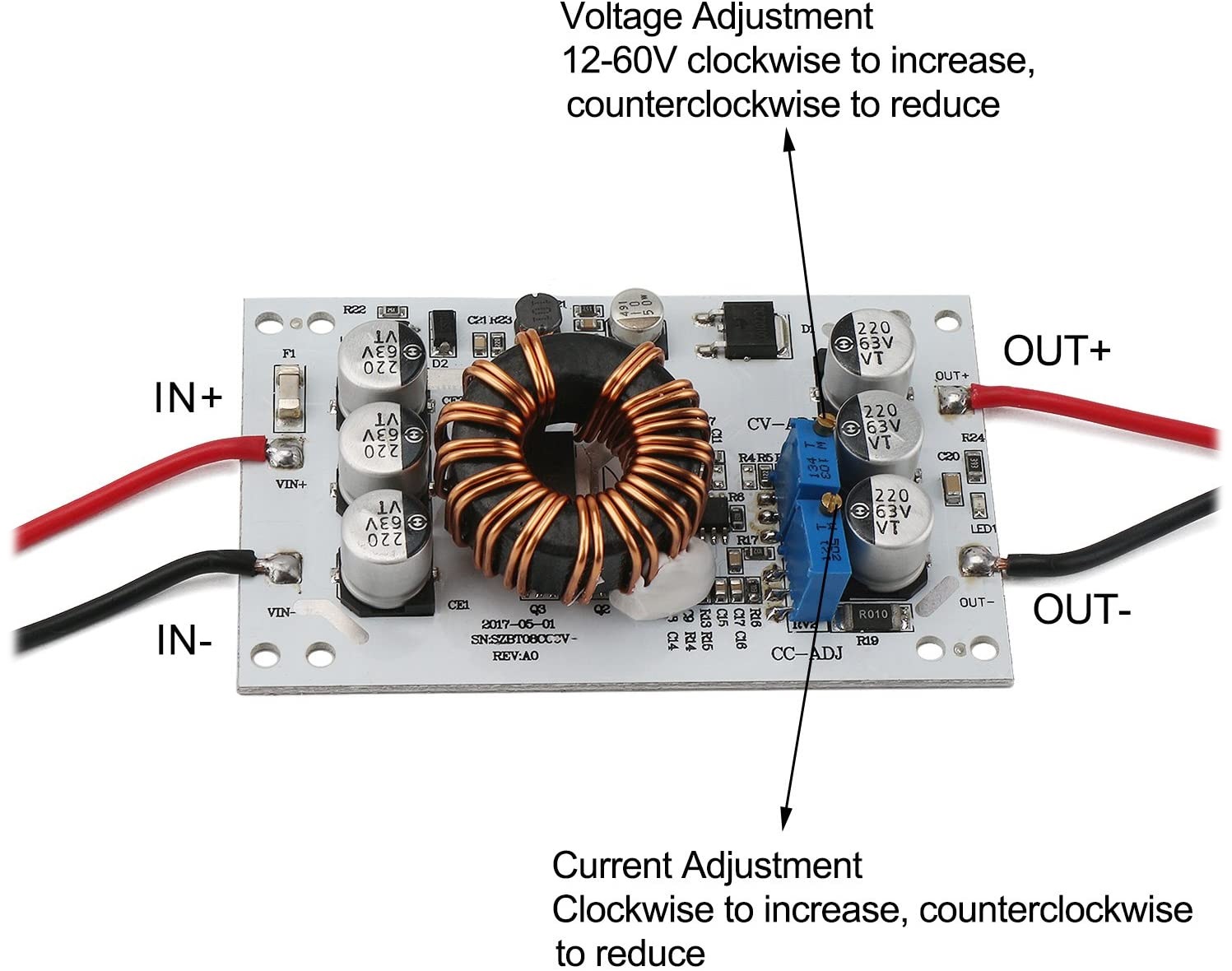
Output Voltage: 12 ~ 60V Continuously Adjustable
Output Current: Maximum output current 10A (adjustable)
Output Power: Active Power P = input voltage V * 10A
Conversion Efficiency: Up to 95% (input voltage, current; output voltage and current affect the conversion efficiency)
Applications
1. DIY an output adjustable vehicle power supply, only need to enter the access 12V power supply, output voltage (14~80V ) free continuously adjustable, but the output voltage can not be lower than the input voltage.
2. Universal car laptop power supply. 12V power input connected to the output regulation voltage into the notebook needs to work.
3. boost charger, you can use the 12V power supply is higher than 12V battery charging, for example, 24V battery, and the charging current can be adjusted.
4. Electronic equipment supply, as long as the voltage to the voltage regulator and the current needs of all can not exceed the rated current working properly.
5. System-level power supply before, when doing a project, the input is 12~18V, 24V power supply system board needs a lot about and the power of ordinary DC-DC module power is too small, then this module will be your best choice, without debugging directly on the machine can work easily achieve high-efficiency power boost.
Module Application Examples
1. Input voltage 12V Current 8.73A, boost output voltage 20V current 5.0A, module efficiency of about 86%, the output voltage, current stability
2. Input voltage 54V Current 13.5A, 58V output current of 12A, use 5Ω1Kw resistance as the load test, the efficiency is 95%
3. Module Output 965W test chart, using 5Ω1Kw resistance as the load test.
Note
1. The input voltage should not be lower than 10V. If the input voltage is too low, the power supply will be damaged.
2. The input/output voltage and current must not exceed the maximum value during operation to avoid damage to the power supply.
3. Pay attention to ventilation and heat dissipation when working for a long time to extend the service life of the power supply.


















دیدگاهها
هیچ دیدگاهی برای این محصول نوشته نشده است.